Stock trading is a fascinating and potentially lucrative field that allows individuals to buy and sell shares of companies on the stock market. This activity can range from short-term trading strategies aimed at making quick profits to long-term investing focused on building wealth over time. Whether you’re a complete beginner or someone looking to refine your trading skills, understanding the basics of stock trading is essential. This article will introduce you to the fundamentals of stock trading, guide you on how to get started, and explain key terminologies you need to know.
Basics of Stock Trading
Understanding Stocks
Stocks represent ownership in a company. When you purchase a stock, you buy a share of that company, making you a partial owner. Companies issue stocks to raise capital for various purposes such as expansion, research and development, or paying off debt. Investors buy these stocks with the expectation that their value will increase over time, allowing them to sell the stocks at a higher price and make a profit.
Stock Exchanges
Stocks are traded on stock exchanges, which are marketplaces where buyers and sellers meet to trade shares. Major stock exchanges include the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) and the NASDAQ. These exchanges provide a regulated and transparent environment for trading, ensuring fair pricing and execution of trades.
Types of Stock Trading
There are different approaches to stock trading, each with its own strategies and goals:
- Day Trading: Involves buying and selling stocks within the same trading day to capitalize on short-term price movements.
- Swing Trading: Focuses on capturing gains in a stock within a short to medium timeframe, usually a few days to weeks.
- Position Trading: Involves holding stocks for a longer period, from several months to years, based on long-term trends.
- Scalping: Aims to make small profits from numerous trades executed in a short period, often minutes.

Risks and Rewards
Stock trading can be highly rewarding but also comes with risks. The value of stocks can fluctuate due to various factors like company performance, economic conditions, and market sentiment. Successful trading requires a good understanding of these factors, risk management techniques, and a disciplined approach.
How to Get Started with Trading
Step 1: Educate Yourself
Before diving into stock trading, it’s crucial to educate yourself about the market. Numerous resources are available, including books, online courses, webinars, and financial news websites. Understanding the basics of stock trading, market analysis, and different trading strategies will give you a solid foundation to start.
Step 2: Choose a Brokerage
To trade stocks, you’ll need to open an account with a brokerage firm. Brokerages act as intermediaries between you and the stock exchange. When choosing a brokerage, consider factors such as:
- Fees and Commissions: Look for a brokerage with low fees and commissions to maximize your profits.
- Trading Platform: Ensure the brokerage offers a user-friendly and reliable trading platform.
- Research and Tools: Access to research reports, analytical tools, and educational resources can be beneficial.
- Customer Service: Good customer service can be crucial, especially when you encounter issues or have questions.
Step 3: Fund Your Account
Once you’ve chosen a brokerage, the next step is to fund your trading account. Most brokerages offer various funding options, including bank transfers, credit/debit cards, and electronic wallets. It’s important to start with an amount you’re comfortable risking, as stock trading involves the possibility of losing money.
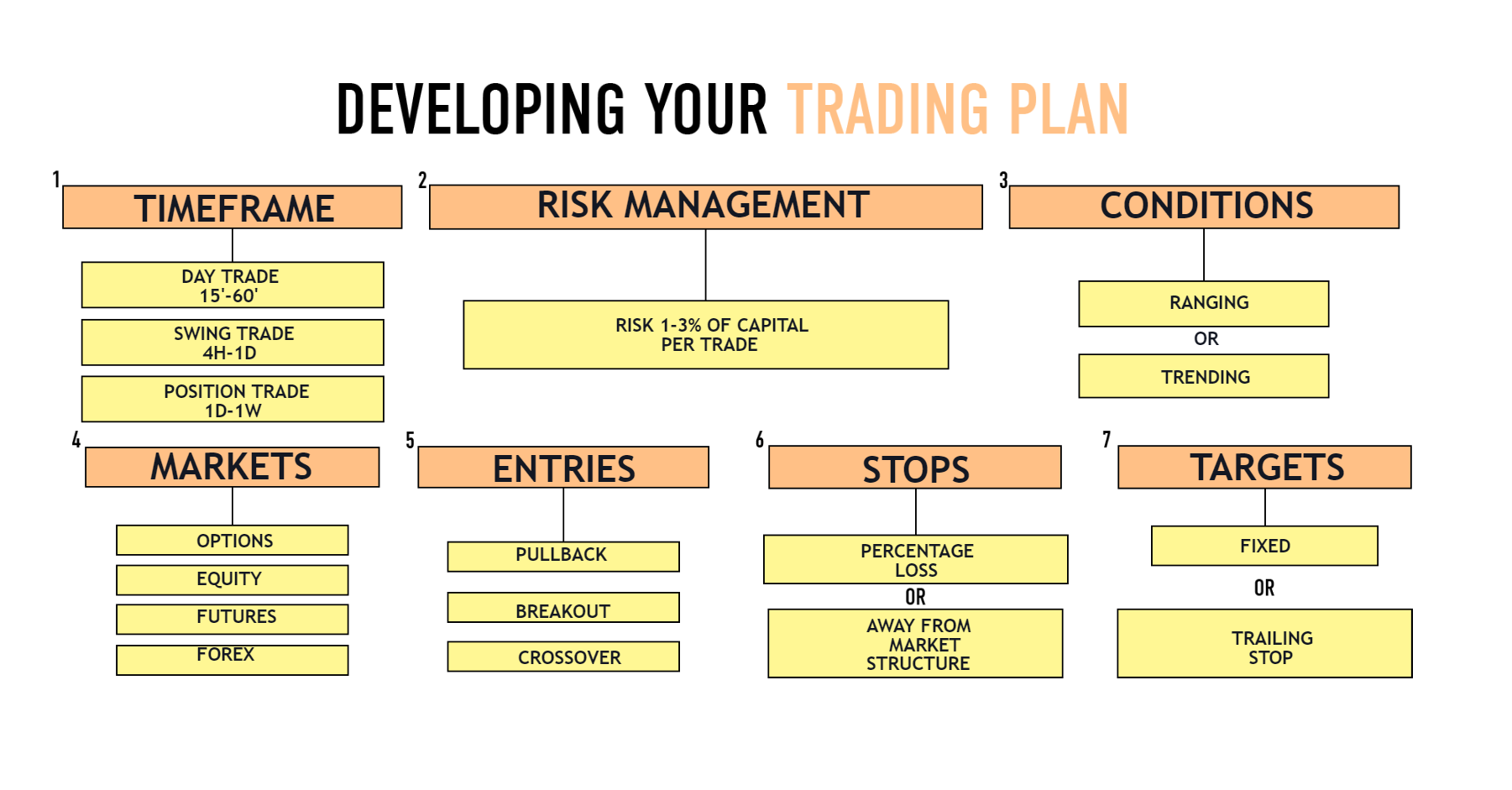
Step 4: Develop a Trading Plan
A well-defined trading plan is essential for success in stock trading. Your plan should include:
- Investment Goals: Define your financial goals, such as saving for retirement, buying a house, or generating supplemental income.
- Risk Tolerance: Assess your risk tolerance to determine how much capital you’re willing to risk on each trade.
- Trading Strategy: Choose a trading strategy that aligns with your goals and risk tolerance.
- Risk Management: Implement risk management techniques, such as setting stop-loss orders to limit potential losses.
Step 5: Start Trading
With your account funded and trading plan in place, you’re ready to start trading. Begin by placing small trades to gain experience and confidence. Monitor the market, keep track of your trades, and continuously learn from your experiences.
Key Terminologies in Stock Trading
Stock Price
The stock price is the amount at which a share of stock is bought or sold. It fluctuates based on supply and demand, company performance, and broader economic factors.
Bid and Ask
- Bid Price: The highest price a buyer is willing to pay for a stock.
- Ask Price: The lowest price a seller is willing to accept for a stock. The difference between the bid and ask price is known as the spread.
Market Order
A market order is an order to buy or sell a stock immediately at the current market price. It ensures the order is executed quickly but doesn’t guarantee the price at which the trade will be executed.
Limit Order
A limit order is an order to buy or sell a stock at a specific price or better. It ensures the trade is executed at the desired price but doesn’t guarantee the order will be filled.
Stop-Loss Order
A stop-loss order is placed to sell a stock once it reaches a certain price, helping to limit potential losses. For example, if you buy a stock at $50 and set a stop-loss order at $45, the stock will be sold if the price drops to $45.
Bull and Bear Markets
- Bull Market: A period when stock prices are generally rising, characterized by investor optimism and economic growth.
- Bear Market: A period when stock prices are generally falling, characterized by investor pessimism and economic slowdown.

Dividend
A dividend is a payment made by a company to its shareholders, usually in the form of cash or additional shares. Dividends are typically paid from the company’s profits and are a way to reward shareholders for their investment.
Portfolio
A portfolio is a collection of investments owned by an individual or institution. Diversifying your portfolio by investing in various assets can help manage risk.
IPO (Initial Public Offering)
An IPO is the process by which a private company goes public by selling its shares to the general public for the first time. It provides the company with access to capital and allows investors to buy shares in the company.
Market Capitalization
Market capitalization, or market cap, is the total value of a company’s outstanding shares of stock. It is calculated by multiplying the stock price by the number of outstanding shares. Market cap helps investors understand the size and value of a company.
Stock trading offers the potential for financial growth and investment opportunities. By understanding the basics, educating yourself, and developing a solid trading plan, you can navigate the stock market with confidence. Remember to start small, learn continuously, and always be mindful of the risks involved. Happy trading!

